Centro de Engenharia e Gestão Industrial
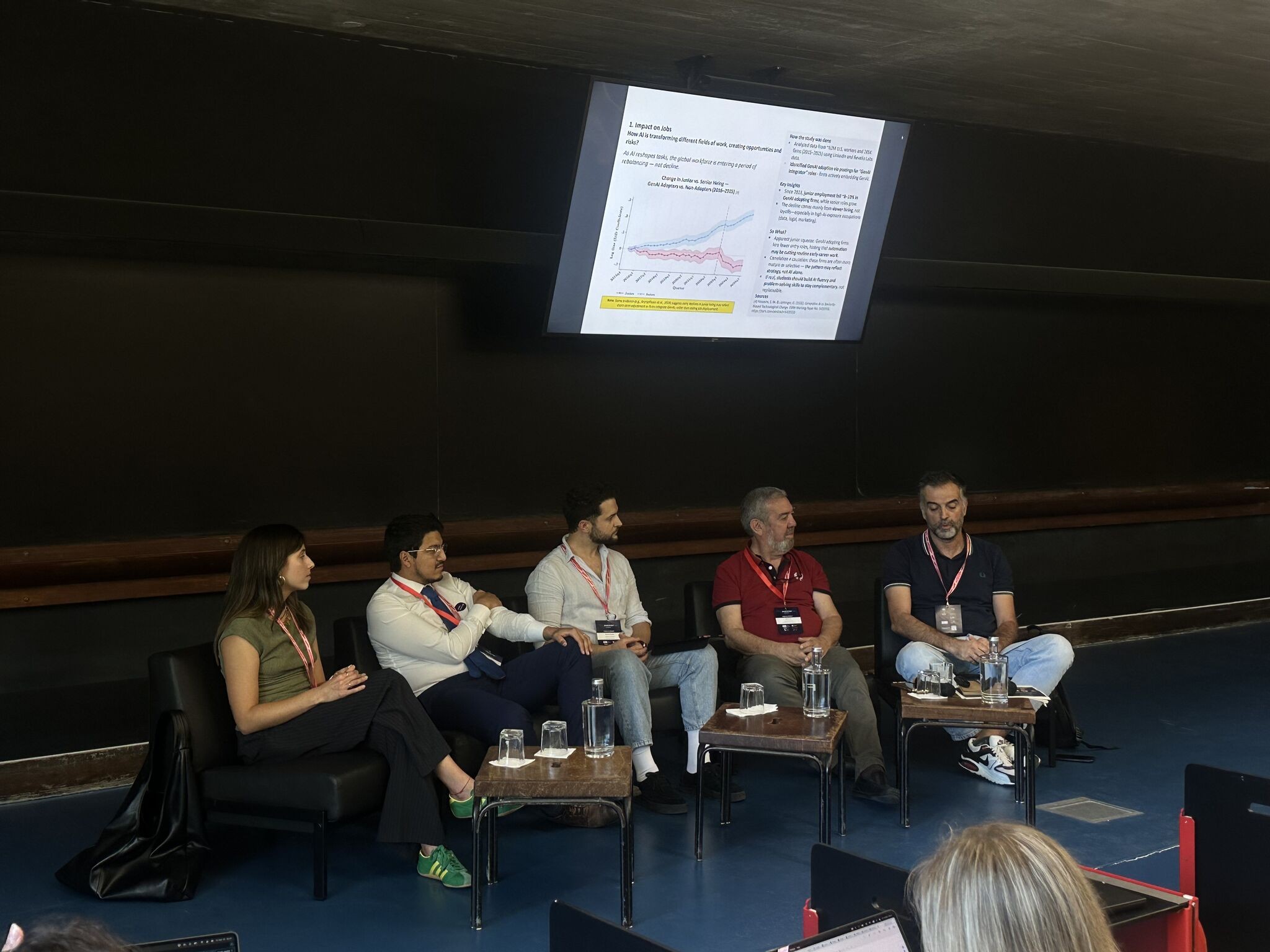
O centro é uma referência internacional em análise de negócios através de sistemas de apoio à decisão para a gestão de serviços e operações, contribuindo, desta forma, para a conceção de serviços, a avaliação de desempenho e a gestão de ativos.
As áreas de aplicação do CEGI incluem Mobilidade/ Transportes, Retalho/Indústria e Saúde. Também se verificam consideráveis contribuições no setor da energia e ainda uma colaboração reforçada com o Centro de Sistemas de Energia.
Nos últimos anos, o CEGI contribuiu substancialmente para as iniciativas da Indústria 4.0 (ao melhorar as regras de programação baseadas nas informações complementares disponíveis nos sistemas de produção).